eno
enolaseBBF10K_001097
source
Escherichia coli str. K-12 substr. MG1655
Catalyzes the reversible conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate into phosphoenolpyruvate. It is essential for the degradation of carbohydrates via glycolysis. It is also a component of the RNA degradosome, a multi-enzyme complex involved in RNA processing and messenger RNA degradation. Its interaction with RNase E is important for the turnover of mRNA, in particular on transcripts encoding enzymes of energy-generating metabolic routes. Its presence in the degradosome is required for the response to excess phosphosugar. May play a regulatory role in the degradation of specific RNAs, such as ptsG mRNA, therefore linking cellular metabolic status with post-translational gene regulation.
attr.
Keoni Gandall
Usage
growth
shipping strain
{shipping_strain}
growth conditions
37 C, shaking 300 rpm
antibiotic
ampicillin
expression
strain
N/A
promoter
N/A
inducer
N/A
cloning
method
GoldenGate
enzyme
BsaI
overhangs
3' - AATG … GCTT - 5'
sequencing
forward primer
M13 For
reverse primer
M13 Rev
Construct
plasmid name
pOpen-eno
plasmid size
3422
insert size
1299
origin
ColE1 High Copy
copy number
500-700
Safety
BSL
BSL1
other information
No Value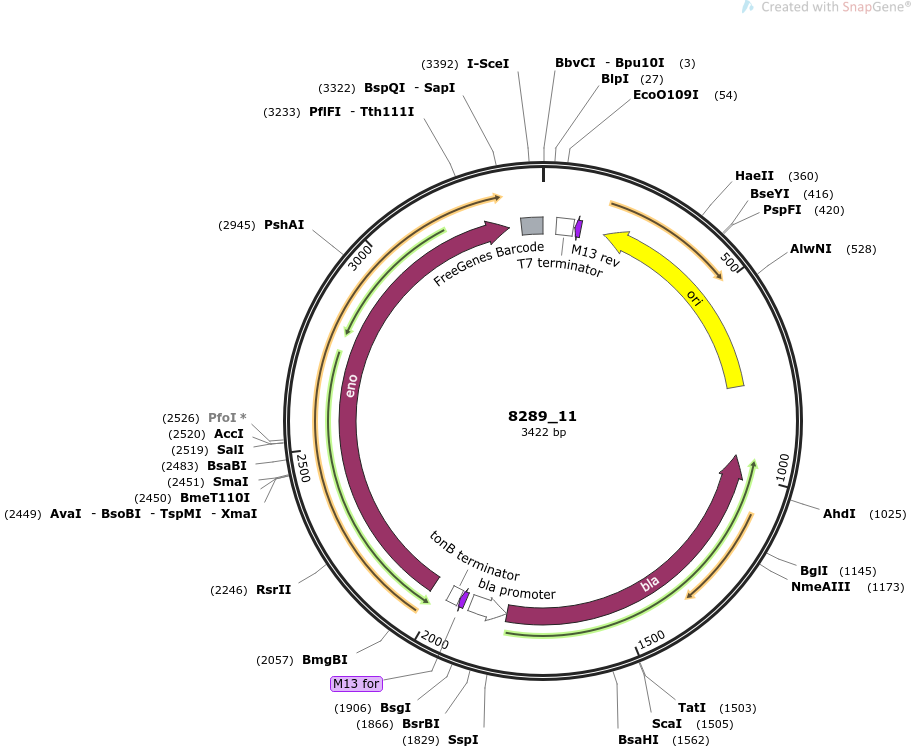
References
Available Elsewhere
FALSE